Are you interested in adopting sustainable eating practices? Discover the benefits, tips, and ethical considerations related to sustainable eating. Learn…
Read More »Healthy Eating
In the world of athletics, a nutritious diet is not just a matter of staying healthy, but also a key component of achieving optimal performance. Healthy Eating for Athletes is essential to fuel their bodies, support muscle growth and recovery, and enhance overall athletic abilities. At Baobei, we understand the importance of prioritizing nutrition for athletes. In this article, we will delve into the fundamental principles of healthy eating for athletes, including nutritional guidelines, pre-workout fueling, post-exercise recovery nutrition, meal planning, and the cautious use of supplements. Let’s explore how adopting a well-balanced diet can empower athletes to thrive in their chosen sports.

| Key Takeaways |
|---|
| 1. A healthy diet is essential for athletes to perform at their best. |
| 2. Nutritional guidelines provide specific recommendations for athletes. |
| 3. Pre-workout fueling and hydration are critical for optimal performance. |
| 4. Proper nutrition after exercise aids in recovery and muscle growth. |
| 5. Meal planning helps athletes create balanced, nutritious meals. |
| 6. The use of supplements should be approached with caution. |
Importance of Healthy Eating for Athletes
Enhanced Performance and Recovery
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in optimizing athletic performance and supporting post-workout recovery. When athletes consume nutritious meals, they provide their bodies with the necessary fuel to perform at their best during training sessions and competitions. Adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats helps enhance endurance, strength, and speed.
- Protein: Essential for muscle repair and growth
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy for physical activities
- Fruits and vegetables: Offer vital vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants for overall health
Injury Prevention
Poor nutrition can increase the risk of injuries among athletes. A diet lacking essential nutrients weakens the immune system, impairs tissue repair, and slows down recovery. By adhering to a balanced eating plan, athletes can strengthen their immune systems, promote tissue healing, and reduce the chances of getting injured.
Mental Well-being
Healthy eating not only benefits the body but also contributes to mental well-being. Nutrient-rich foods stimulate the production of brain chemicals that regulate mood and help manage stress. Consuming balanced meals with adequate omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals can improve cognitive function, focus, and concentration in athletes.
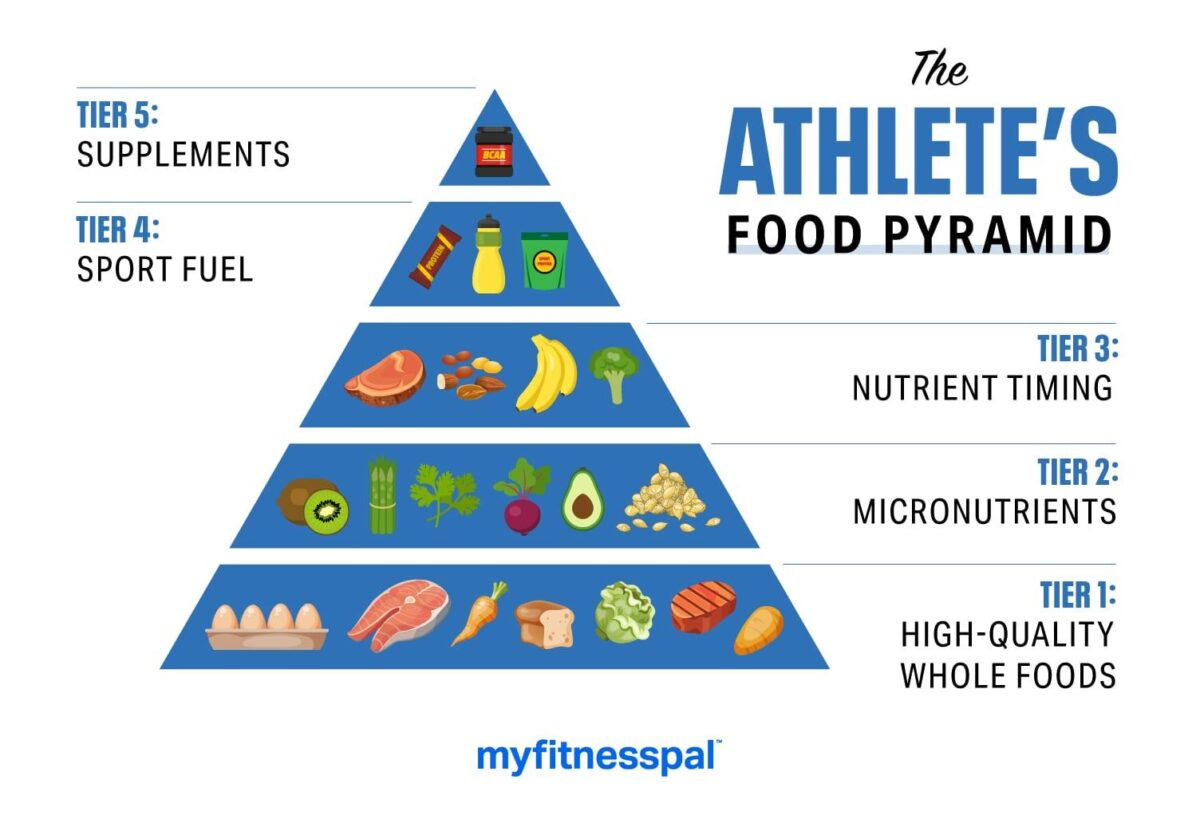
Nutritional Guidelines for Athletes
The Role of Macronutrients
Macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, play a vital role in an athlete’s diet. Each macronutrient provides different benefits and should be consumed in the right proportions to support optimal performance.
- Carbohydrates: These are the primary source of energy for athletes. It’s important to include both complex carbohydrates (such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables) and simple carbohydrates (found in foods like sports drinks and energy gels) in your diet.
- Proteins: Protein is crucial for muscle repair and growth. Athletes should aim to consume lean sources of protein, such as poultry, fish, beans, and low-fat dairy products.
- Fats: Healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, provide long-lasting energy and support the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. It’s important to choose unsaturated fats and limit saturated and trans fats.
The Importance of Micronutrients
While macronutrients get a lot of attention, micronutrients are equally important for an athlete’s overall health and performance. These include vitamins and minerals that support various bodily functions.
- Calcium: Crucial for strong bones and muscle function. Good sources include dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods.
- Iron: Needed for oxygen transportation throughout the body. Include iron-rich foods like lean red meat, poultry, fish, and legumes.
- Vitamin D: Aids in calcium absorption and supports immune function. Get vitamin D from sunlight exposure, fatty fish, and fortified products.
- B vitamins: Essential for energy metabolism. Include whole grains, lean meats, and leafy greens in your diet to ensure an adequate intake.
Hydration for Optimal Performance
Proper hydration is crucial for athletes to maintain performance and prevent dehydration. Aim to drink fluids throughout the day, not just during exercise, and consider the following hydration tips:
- Drink water before, during, and after physical activity to replace fluids lost through sweat.
- Monitor urine color as an indicator of hydration status. Pale yellow urine usually indicates adequate hydration.
- Include electrolyte-rich beverages, such as sports drinks, during prolonged intense exercise or high heat conditions to replenish electrolytes lost through sweat.
| Sample Meal Plan for Athletes | Meal | Food Choices |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Scrambled eggs with whole wheat toast and fruits | – 3 scrambled eggs – 2 slices of whole wheat toast – Mixed fruits (e.g., berries, banana) |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad with quinoa | – Grilled chicken breast – Mixed greens and vegetables – Cooked quinoa |
| Snack | Greek yogurt with nuts and seeds | – 1 cup of Greek yogurt – Mixed nuts and seeds (e.g., almonds, chia seeds) |
| Dinner | Salmon with roasted vegetables and brown rice | – Grilled salmon fillet – Assorted roasted vegetables – Cooked brown rice |

Pre-Workout Fueling and Hydration
The Importance of Pre-Workout Nutrition
Proper pre-workout fueling is essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent fatigue during training or competition. Eating the right foods before exercise provides the body with the necessary energy and nutrients to perform at its best. Carbohydrates are particularly important, as they are the main source of fuel for the muscles. Including high-quality carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables in your pre-workout meal can help sustain energy levels and improve endurance.
Hydration for Peak Performance
Hydration is another key aspect of pre-workout preparation. Adequate fluid intake before exercise is crucial to regulate body temperature, lubricate joints, and transport nutrients to cells. It is recommended to consume about 500 milliliters to 1 liter of water or a sports drink 2 to 3 hours before your workout. Additionally, it’s important to sip on fluids throughout the day leading up to your training session, especially if you are exercising in a hot or humid environment.
Pre-Workout Snack Ideas
When it comes to pre-workout snacks, choosing the right combination of macronutrients is key. Ideally, your snack should contain carbohydrates for energy, protein for muscle repair and growth, and a small amount of healthy fats for satiety. Here are some example pre-workout snack ideas:
- Whole grain toast with peanut butter and banana slices
- Greek yogurt topped with berries and a sprinkle of granola
- Oatmeal with a scoop of protein powder and mixed nuts
| Benefits of Pre-Workout Fueling and Hydration | Examples |
|---|---|
| Enhanced energy levels and endurance | Whole grain toast with peanut butter and banana slices |
| Improved muscle repair and growth | Greek yogurt topped with berries and a sprinkle of granola |
| Sustained energy throughout the workout | Oatmeal with a scoop of protein powder and mixed nuts |

Post-Exercise Recovery Nutrition
Importance of Nutrient Timing
Proper nutrition after exercise is key to replenishing energy stores and promoting muscle recovery. Consuming the right nutrients at the right time can enhance the body’s ability to repair and rebuild, maximizing the benefits of the workout. One of the most important aspects of post-exercise nutrition is nutrient timing.
- Timing is crucial: Aim to consume a post-workout meal or snack within 30-60 minutes after exercise.
- Carbohydrates for energy: Include carbohydrates in your post-workout meal to replenish glycogen stores and provide energy for future workouts. Good options include fruits, whole grains, or potatoes.
- Protein for muscle repair: Incorporate protein-rich foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, or legumes to support muscle recovery and growth.
- Hydration is key: Remember to rehydrate by drinking plenty of fluids, such as water or a sports drink, to replace what was lost during exercise.
Optimizing Macronutrient Ratios
While nutrient timing is important, the macronutrient composition of your post-workout meal also plays a significant role in recovery. Striking the right balance between carbohydrates, protein, and fat can enhance muscle repair, reduce muscle breakdown, and promote overall recovery.
- Carbohydrates: Aim for a ratio of approximately 3:1 or 4:1 of carbohydrates to protein in your post-workout meal. This helps replenish glycogen stores and stimulates insulin release, which aids in nutrient absorption.
- Protein: Include high-quality protein sources like chicken, fish, or tofu to provide essential amino acids for muscle repair and growth. Aim for around 20-30 grams of protein in your post-workout meal.
- Fat: While fat should be consumed in moderation after exercise, incorporating sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, or olive oil can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.

Meal Planning for Athletes
Create a Balanced Meal
When planning meals for athletes, it’s essential to focus on creating a well-balanced plate that provides the necessary nutrients for optimal performance. Start by including a source of lean protein such as chicken, fish, or tofu. Protein helps repair and build muscle tissue. Next, add a variety of colorful vegetables that are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These can include broccoli, bell peppers, spinach, and carrots. Additionally, include a serving of whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, or whole wheat bread to provide energy for workouts and training sessions. Lastly, don’t forget to add a healthy source of fat such as avocados, nuts, or olive oil to support overall health.
Sample Balanced Meal:
- Grilled chicken breast
- Steamed broccoli and bell peppers
- Quinoa
- Sliced avocado
Plan Ahead and Prep
Meal planning is key for athletes to ensure they have nutritious meals readily available. A great strategy is to set aside some time each week to plan your meals and do the necessary food prep. This could involve washing and chopping vegetables, marinating meats, or cooking in bulk and portioning out your meals for the week. By planning ahead, you can avoid relying on unhealthy convenience foods when you’re pressed for time. Another helpful tip is to pack snacks and meals in advance to take with you to practices, games, or competitions. This way, you’ll have nutritious options on hand to fuel your body and prevent hunger-induced poor food choices.

Supplements for Athletes
When it comes to supplements for athletes, it is important to approach them with caution and consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian. While some supplements can be beneficial for enhancing performance and aiding recovery, others may be ineffective or even harmful.
1. Performance-Enhancing Supplements
Performance-enhancing supplements are designed to improve athletic performance and may include substances like creatine, caffeine, and beta-alanine. These supplements can provide a boost in strength, endurance, and focus, but their effectiveness can vary depending on the individual.
- Creatine: This supplement helps increase muscle strength and power, particularly during high-intensity, short-duration activities.
- Caffeine: A common stimulant that can enhance endurance and reduce fatigue during prolonged exercise.
- Beta-Alanine: Known to improve muscle endurance by reducing the accumulation of lactic acid.
2. Recovery Supplements
Recovery supplements are aimed at aiding the body’s recovery process after intense exercise, reducing muscle soreness, and promoting tissue repair. Here are some key recovery supplements commonly used by athletes:
- Protein Powders: Whey, casein, and plant-based protein powders can help replenish muscles and promote muscle repair.
- BCAAs (Branched-chain amino acids): Essential amino acids that play a role in muscle protein synthesis and can help prevent muscle breakdown.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Possess anti-inflammatory properties and can aid in reducing exercise-induced inflammation.
3. Nutritional Gaps and Micronutrients
Athletes may have increased nutritional needs due to the demands of their training. The use of supplements can help bridge the nutritional gaps and ensure adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals. Here are some commonly used supplements:
- Multivitamins: Provide a wide range of vitamins and minerals to support overall health and well-being.
- Vitamin D: Important for bone health, immune function, and muscle strength.
- Iron: Essential for oxygen transport and preventing anemia.
4. Considerations and Risks
While supplements can be beneficial, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and considerations:
- Quality and Regulation: Not all supplements are held to the same standards, so choose reputable brands that undergo third-party testing for quality and purity.
- Possible Side Effects: Some supplements may cause adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal distress or allergic reactions.
- Drug Interactions: Certain supplements can interact with medications, so it’s important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Conclusion
Eating a healthy diet is not only important for overall health, but it also plays a significant role in the performance and success of athletes. By following the nutritional guidelines, athletes can ensure they are consuming the right balance of macronutrients and micronutrients to meet their energy needs and support their training. Pre-workout fueling and hydration can enhance performance and prevent fatigue, while post-exercise recovery nutrition aids in muscle repair and growth. By incorporating meal planning strategies, athletes can create balanced and nutritious meals to fuel their bodies effectively. However, it is crucial to approach the use of supplements with caution and consult with a healthcare professional to determine their necessity.
By prioritizing healthy eating habits and making informed dietary choices, athletes can optimize their performance, improve their overall health, and excel in their respective sports.
In this article, we delve into the topic of nutrient deficiencies and diet. We explore the impact of nutrient deficiencies…
Read More »Discover the numerous benefits of seasonal eating and nutrition. Explore a guide to the best fruits and vegetables for each…
Read More »Looking for healthy alternatives to traditional dairy products? Explore the world of dairy alternatives for better nutrition and health. Discover…
Read More »Fiber plays a crucial role in a healthy diet, offering a range of benefits. Learn about the importance of dietary…
Read More »



